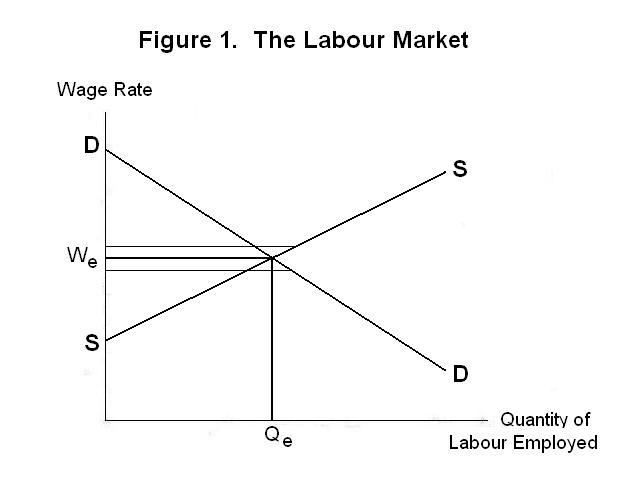
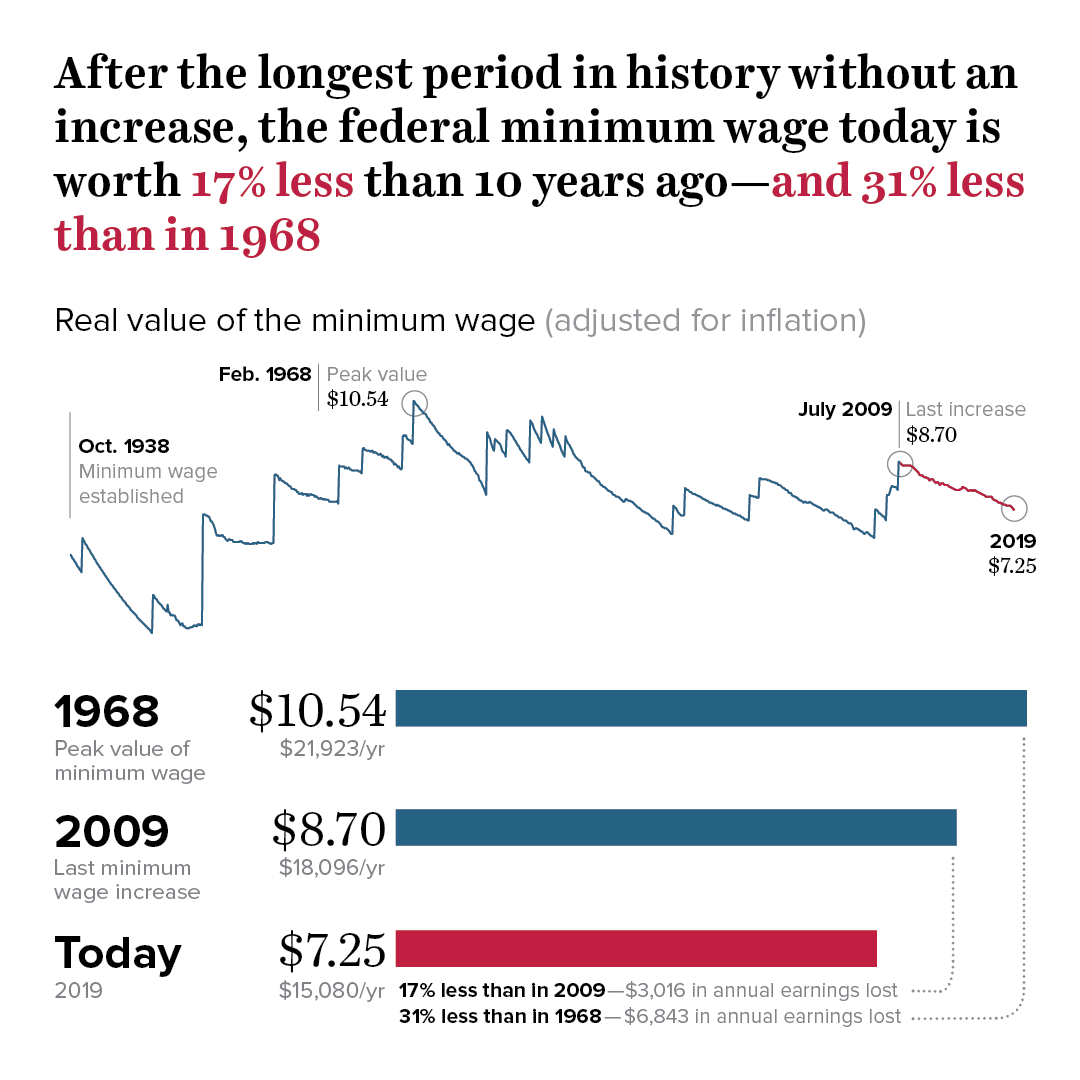The market clearing price wage for unskilled labor equates the quantity demanded by employers with the quantity supplied by unskilled workers.
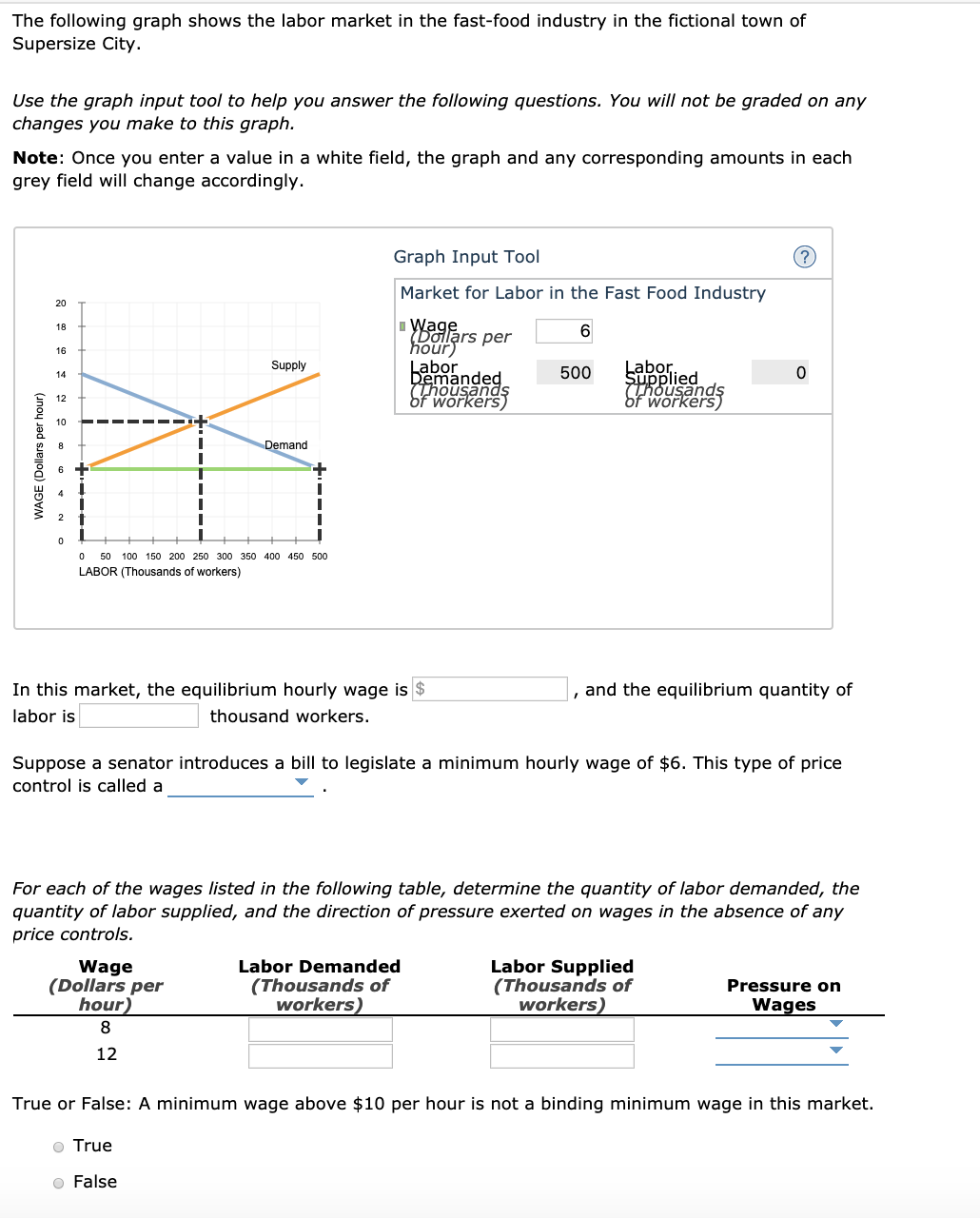
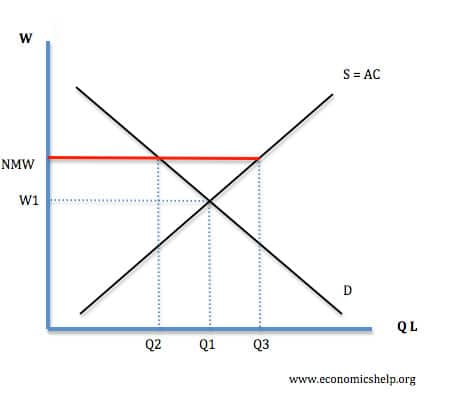
Graph of wages and labor indicating price floor.
If the government sets a floor above the market clearing level then it will induce a surplus of unskilled labor.
This is a minimum price in the market.
When we talked about rent control that was a price ceiling.
It has to be at least 7 an hour so this right over here is a price floor.
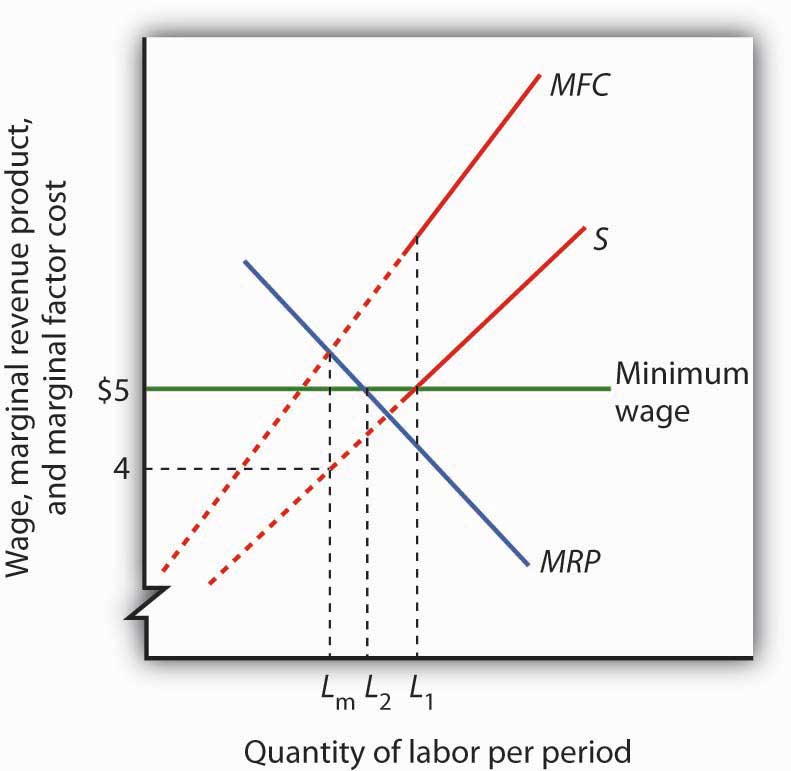
For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price.
In this case the price which is typically on the y axis is the wage which gets paid to workers.
A price floor graph.
Since the price floor this minimum price is higher than the actual clearing price.
The most common example of a price floor is the minimum wage.
The opposite of a price floor is a price ceiling.
That was a maximum price for rent now this is a minimum price for labor.
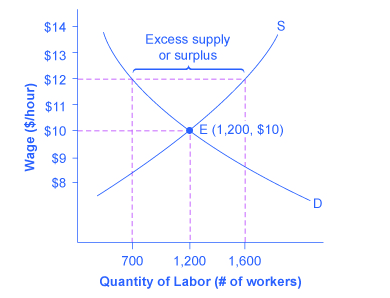
Imposing a wage floor at 12 hour leads to an excess supply of labor.
In this simplistic model it is best to think of the wage as how much a firm pays to get one worker.
We saw that a price floor in the labor market that s a minimum wage already creates a surplus of labor that shows up as unemployment.
Example of a price floor the original equilibrium in this labor market is a wage of 10 hour and a quantity of 1 200 workers shown at point e.
Department of labor enforces the fair labor standards act flsa which sets basic minimum wage and overtime pay standards.
Minimum wage the federal minimum wage is 7 25 per hour for workers covered by the flsa.
This is the minimum price that employers can pay workers for their labor.